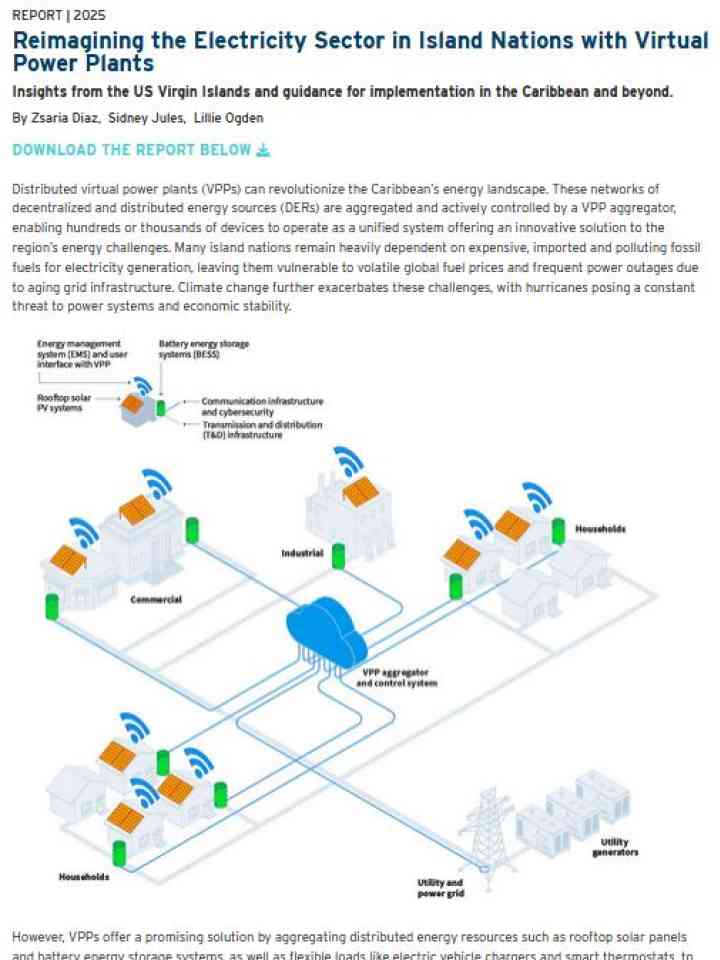
Reimagining the electricity sector in island nations with virtual power plants
This report explores the potential of Distributed Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) to transform the Caribbean’s energy landscape. It highlights how these systems aggregate decentralized energy resources—like rooftop solar panels, batteries, and smart loads—into a unified, actively managed network. By doing so, VPPs offer an innovative approach to improving energy resilience, reducing costs, and enhancing grid flexibility across island nations that are currently dependent on expensive and polluting fossil fuels. The report focuses on how VPPs can strengthen disaster preparedness and support clean energy transitions, with a detailed case study from the US Virgin Islands.
The report finds that implementing VPPs in the US Virgin Islands significantly boosts energy reliability and reduces grid vulnerability to hurricanes and power outages. VPPs stabilize energy supply through decentralized sources, lower electricity costs, and increase energy independence. The report concludes that the VPP model is scalable across the Caribbean, provided that country-specific strategies are adopted. Recommendations are offered for policymakers and utility providers to accelerate VPP adoption, emphasizing their role in climate mitigation and sustainable development. Overall, VPPs are presented as a critical tool for advancing energy resilience and achieving long-term energy sustainability in small island developing states.
Explore further